Mount Everest is singing for joy. Everyone else is worried
The Economist Magazine
“MOUNT EVEREST is singing for joy and the Brahmaputra River swirling with happiness”. Or so says an official Chinese newspaper (using the Tibetan names, Qomolangma and the Yarlung Tsangpo). After much delay, China has started to extend its controversial railway line in Tibet that will draw more tourists to the mountain and boost trade with South Asia. How happy the outcome will be is not so clear.
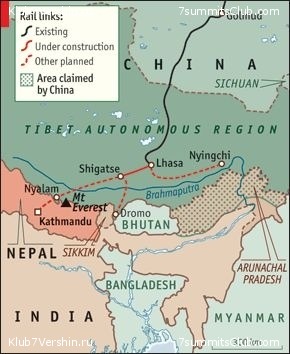
Planning for the 253km (157-mile) line from the Tibetan capital, Lhasa, to the region’s second city, Shigatse, began in 2002, four years before Lhasa itself was connected to China’s railway network. The authorities appear not have been deterred by the problems that the railway brought to Lhasa. A tourism boom and a flood of immigrants from China’s interior contributed to an explosion of unrest among embittered Tibetans in March 2008. The launch ceremony in Lhasa of the $2 billion extension on September 26th was celebrated by dancing children in elaborate Tibetan costumes. Chinese television said the line would be of “great significance for the strengthening of ethnic unity”.
Like the route to Lhasa, which crossed the highest terrain of any railway in the world, the single-track extension will involve considerable technical difficulties. Nearly half of it will go through tunnels or over bridges (96 of them). It will cross areas prone to earthquakes, landslides and sand storms. Whereas the line to Lhasa had to traverse unstable permafrost, the new one will be challenged by geothermal fields with hot springs. All this at an oxygen-starved altitude of 3,550-4,000 metres.
The railway will make it easier to reach Mount Everest, which can expect to see a lot more tourists eager to be photographed in front of the world’s highest peak (Shigatse is also due to open an airport soon, Tibet’s fifth for civilian use). In 2007 the Chinese side of the mountain recorded 27,476 visits by Chinese tourists, almost twice as many as in 2006, after the new rail service to Lhasa had opened. Environmentalists are worried.
Shadows over Qomolangma
So are the Indians. The government in Delhi has been nervously watching China’s build-up of infrastructure in Tibet. The extension to Shigatse, besides facilitating military movements near China’s border with India, is likely to boost trade with Nepal, where the two giants are vying for influence in a power struggle that is still going on. China has long-term plans for more extensions of the line, to Nyalam on the border with Nepal and to Dromo near Bhutan and the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal wants the railway extended to Kathmandu, which India fears would give China more clout in a country India sees as part of its sphere of influence. Another proposed line, from Lhasa east to Nyingchi, would bring the network close to the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh, most of which China claims.
Tibetans might have mixed feelings too. The rail link to Lhasa brought disproportionate benefits to ethnic Han Chinese whose language and culture enabled them to take quicker advantage of the Han tourist influx. Tibet Business News said the majority of traders in Shigatse were migrants from beyond Tibet. It quoted a woman from neighbouring Sichuan Province saying that the railway would cut her costs of doing business in Shigatse by half. Expect more like her to come.
Correction: An earlier version of this article had it that “most of China” claims the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. Rather, (all of) China claims most of Arunachal Pradesh. This article was corrected on October 8th, 2010.
The Economist. Full text >>>>>>>
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
China official information
LHASA, Sept. 26 (Xinhua) -- China began work on Sunday to build an extension to the world's highest rail link, the Qinghai-Tibet Railway, linking Xigaze, the second largest city in the southwestern Tibet Autonomous Region.
The 253-km line from Tibet's capital Lhasa to Xigaze will pass through five counties as well as over the 90-km long Yarlung Zangbo Grand Canyon.
The work will take about four years.
This is the first extension of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway that opened in July 2006.
The Lhasa-Xigaze railway, with a budget of 13.3 billion yuan (1.95 billion U.S. dollars), is capable of transporting 8.3 million tonnes of cargo per year. The local authorities did not provide a projected annual passenger number.
Zhang Qingli, Communist Party chief of Tibet, said the rail line would make train services available in southwestern Tibetan regions which currently rely solely on roads for transport.
The railway will detour around nature reserves and drinking water sources and more measures will be taken during construction to better protect the fragile plateau environment, Zhang said.
Minister of Railways Liu Zhijun said the extension is a key project in China's long and medium-term railway network expansion and will speed up Tibet's social and economic development.
It will also play a vital role in boosting tourism and promoting the rational use of resources along the line, he said.
Further, Tibet is planning to build another railway to link Lhasa with Nyingchi to boost tourism and the economy in Tibet.
During its four-year operation, the Qinghai-Tibet Railway has reduced transportation costs and greatly boosted economic growth in Tibet, especially through developing tourism and other local special resources, Liu said.
Xigaze, with a history of more than 600 years, is Tibet's second largest city and the traditional seat of the Panchen Lamas.
Xigaze City is the administrative center of the Tibetan prefecture of the same name, a 182,000 square km area that borders India, Nepal and Bhutan. It is also famous for Qomolangma (known as Mount Everest in the West), which rises up from within it.